What Is Cyber Defamation? Meaning, Laws & Online Liability
Online communication has made reputation more fragile than ever. Knowing what is cyber defamation is essential for anyone using the internet today. Cyber defamation meaning includes any false or harmful statement shared online that damages a person or business. With digital platforms growing rapidly, Indian courts now rely on updated laws—especially cyber defamation under the IT Act 2000—to tackle the rising number of online defamation cases.
Definition and Impact of Cyber Defamation
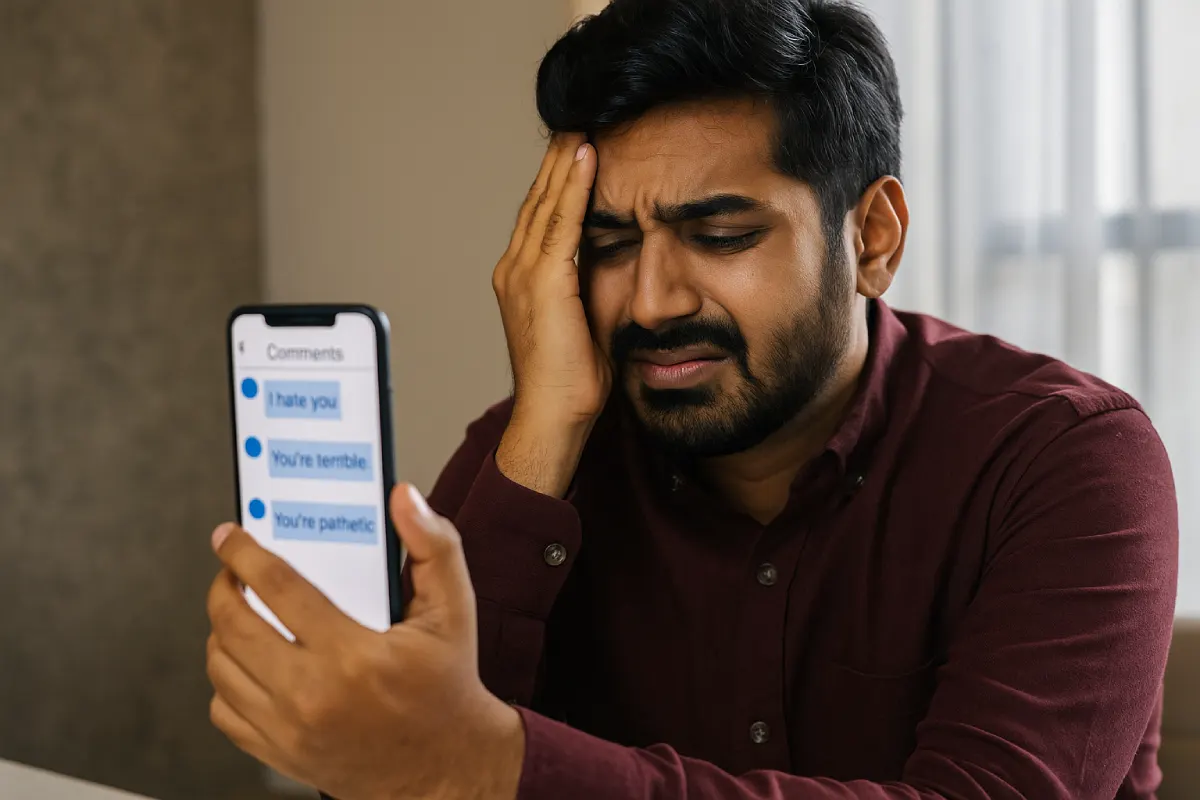

What is Cyber Defamation?
Cyber defamation refers to publishing false or damaging statements about an individual or organization through digital means such as social media, emails, blogs, or websites. It mirrors traditional defamation but occurs in the virtual world.
Consequences
The consequences can be devastating — loss of reputation, professional setbacks, mental distress, and in severe cases, financial loss. In the age of the internet, defamatory statements can spread globally within seconds, causing irreversible harm.
Traditional Defamation Basis
Under Sections 499 and 500 IPC, defamation includes any written, spoken, or visual publication that harms reputation. Today, cyber defamation under IT Act 2000 extends the law to digital platforms, closing gaps left by traditional defamation rules.
Types of Cyber Defamation
Cyber defamation can take several forms, depending on the mode and intention behind the act.

Slander and Libel
When defamatory statements are made verbally in online videos or written in posts or articles, they constitute slander and libel, respectively.
Cyberbullying
Persistent online harassment targeting an individual with insults or false accusations can qualify as defamation, especially if it harms their social or professional standing.
Revenge Porn
Sharing intimate or private photos or videos without consent to harm someone’s reputation is both defamation and a cybercrime under Sections 66E and 67A of the IT Act.
False Reviews and Allegations
Posting fake reviews or accusations online that damage a business or professional reputation can also be treated as defamation.
Impersonation and Doxing
Creating fake profiles, spreading false information under someone else’s name, or revealing private data (doxing) can lead to legal consequences.
Hate Speech and Harassment
Defamatory hate speech that targets individuals or groups based on identity or beliefs also falls under cyber defamation.
Legal Liability for Cyber Defamation in India
Understanding the legal framework for cyber defamation in India is essential for both victims and digital platforms. This section outlines how Indian laws, such as the IPC and the Information Technology Act, 2000, hold individuals and intermediaries accountable for defamatory content shared online.
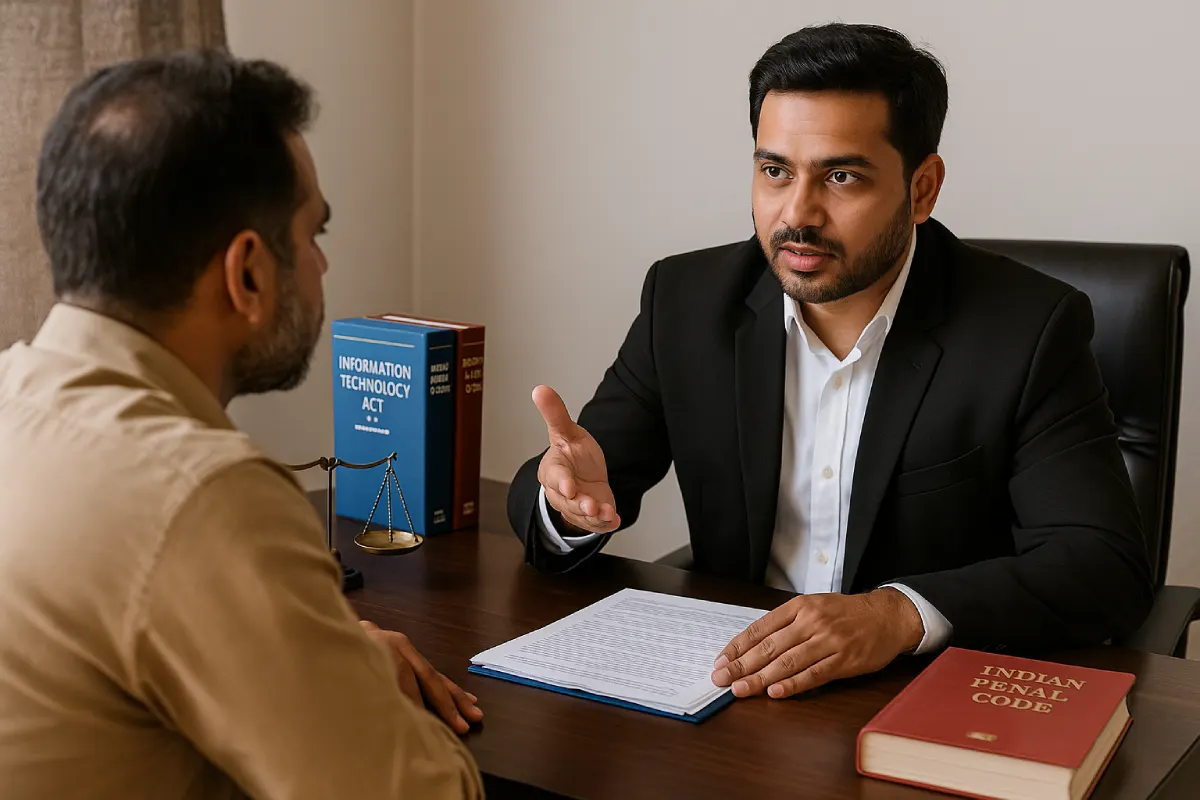

Indian Penal Code (IPC)
Sections 499 and 500 IPC apply directly to digital defamation. Offenders may face imprisonment for up to two years, a fine, or both.
Information Technology Act, 2000
Sections 66A (now repealed) and 67 of the IT Act address offenses involving obscene or offensive online material. Currently, Section 66D (cheating by impersonation using computer resources) and Section 67A (publishing sexually explicit material) are invoked in relevant cases.
Intermediary Guidelines (2021)
Under these rules, social media platforms must remove defamatory or illegal content once notified. Failure to comply can make intermediaries liable. The official Intermediary Guidelines 2021 – duties of platforms document explains platform obligations and takedown procedures.
Reporting and Enforcement
Victims should immediately report abuse to social media platforms using their in‑app reporting tools. This helps initiate faster takedown of defamatory posts and strengthens your evidence trail. Victims can report cyber defamation online via the National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal. Strong cybersecurity measures also help prevent impersonation and defamatory attacks.
You can also learn how to unfreeze a bank account from cybercrime if it’s linked to online fraud or defamation.
Cyber Defamation in Cybersecurity
Despite clear laws, prosecuting cyber defamation remains complex.
Identifying the Perpetrator
Online anonymity makes it difficult to trace the offender, especially when the content originates from foreign servers.
Speed and Volume of Dissemination
The viral nature of social media makes controlling the spread of defamatory content challenging.
Jurisdictional Issues
Defamation cases can involve multiple jurisdictions since the content can be accessed globally. Indian courts apply principles of territorial nexus to establish jurisdiction.
Balancing Rights
Courts often have to balance between protecting freedom of speech under Article 19(1)(a) and the right to reputation under Article 21 of the Constitution. Cybersecurity plays a key role today in preventing impersonation, detecting fake profiles, and securing digital identities.
Evidence and Admissibility
Indian Evidence Act
Sections 65A and 65B of the Indian Evidence Act, 1872, govern the admissibility of electronic evidence such as screenshots, emails, or digital records.
Forms of Evidence Admissible
- Social media posts or comments
- Emails or chat logs
- Server or IP address data
- Forensic digital reports
Proper certification under Section 65B(4) is mandatory to ensure admissibility in court.
Major Cyber Defamation Case Laws in India
1. Kalandi Charan Lenka vs State of Odisha (2017)
In this case, the accused created a fake Facebook account and posted obscene material targeting the victim. The court recognized this as cyber defamation and a violation under both IPC and IT Act provisions.
2. Rajiv Dinesh Gadkari vs Smt. Nilangi Rajiv Gadkari (2016)
The Bombay High Court observed that posting false and derogatory content on social media amounts to defamation, setting a precedent for online reputation protection.
3. SMC Ltd. v. Jogesh Kwatra (2001)
This was India’s first recognized case of cyber defamation, where an employee sent defamatory emails about the company. The Delhi High Court issued an injunction restraining the accused from further communication, establishing the legal recognition of cyber defamation in India.
Real-World Impact and Reputational Damage
Cyber defamation can affect individuals, brands, and organizations alike. With the internet’s permanence, defamatory content can cause lasting reputational damage. Businesses face customer distrust, while individuals suffer emotional and social consequences. Legal remedies provide recourse, but prevention through awareness and responsible online behavior remains key.
To understand how legal experts can protect your online reputation, explore our experienced criminal lawyers in Bangalore.
FAQs
What is the punishment for online defamation?
Under Section 500 IPC, the punishment for defamation includes imprisonment up to two years, a fine, or both.
What evidence is needed in cyber defamation cases?
Digital records such as emails, screenshots, or chat logs certified under Section 65B of the Evidence Act are admissible.
Which case law is famous for defamation?
The case of SMC Ltd. v. Jogesh Kwatra (2001) is one of India’s most cited cyber defamation cases.
What is an example of cyber defamation?
Publishing false accusations or spreading harmful rumors about someone on social media or digital platforms is a common example of cyber defamation.
Conclusion
Cyber defamation can ruin reputations and mental peace within moments. If you’ve been targeted online or your reputation has been unfairly damaged, swift legal action can help. At Prashastha Legal, our experienced lawyers specialize in cyber defamation law and digital reputation defense.
Contact Prashastha Legal today for expert advice, evidence preservation, and strong representation in defamation and cybercrime cases. Safeguard your name — because your reputation deserves protection.